
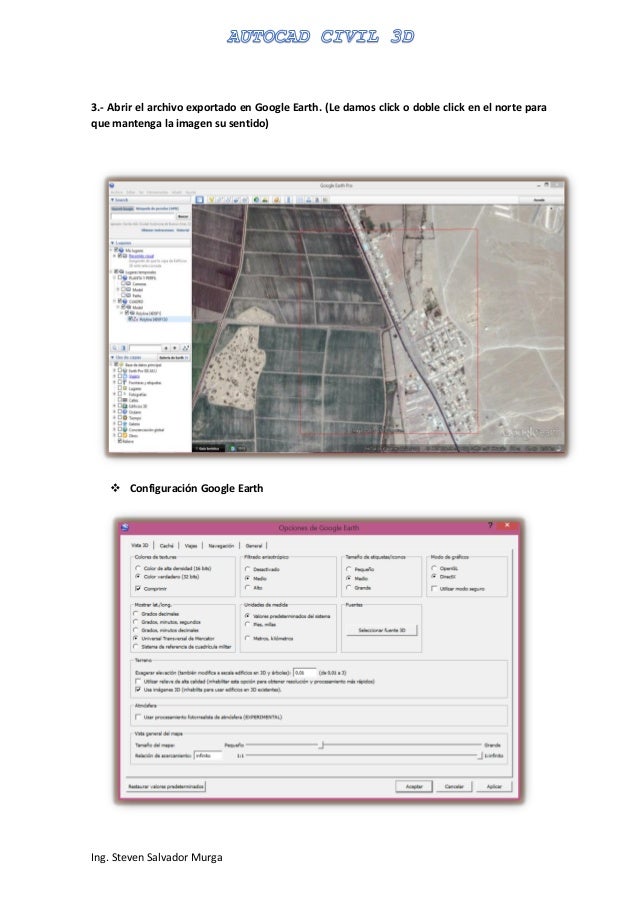
- #Naural earth raster in r how to#
- #Naural earth raster in r full#
- #Naural earth raster in r code#
- #Naural earth raster in r download#
- #Naural earth raster in r free#
#Naural earth raster in r download#
You can browse our maps or download the data to make your.
#Naural earth raster in r free#
Free GIS Data SourcesĮverybody who is really interested to play with the geographical data these is the free resource providing platforms. GADM provides maps and spatial data for all countries and their sub-divisions. You will need the raster and ggplot2 packages installed. This layout is usually used for satellite imagery, aerial photography, digital elevation models and topographic maps, etc. Recently I moved from ArcMap to R do a lot of my spatial analysis and map making. Raster data is a bitmap representation such as a TIFF or JPEG. If vector data is non-figurative, raster data is factual.
#Naural earth raster in r how to#
That column contains one or additional coordinates that illustrate how to portray the point, line or polygon that represents that feature on the features of the terrain. returns downloaded data as a spatial object or the filename if loadFALSE. Natural Earth is a public domain map dataset available at 1:10 million (1 cm 100 km), 1:50 million, and 1:110 million map scales.
/https://syrinscape-us.s3.amazonaws.com/media/dd/product/images/6f92351cbb0a1318ea0374870f0bd6f6.jpg)
The better way to visualize it is to believe it as a spreadsheet with columns that include our regular data, but in count it always has an additional column called “geometry”. Pseudocylindrical projections are better suited for presenting raster data because their arcing meridians converge toward the poles, compress- ing the size of. download data from Natural Earth and (optionally) read into R. We can assume vector data as guidelines for how to render the data. Hello, In my case I have a k-means classification in R and the class were classification in values into 1 to 5. We know that there are 2 major types of GIS data: I am trying to render the world map with elevation data using D3. Environmental Analysis and Modelling Using GIS Aligning Natural Earth Geojson and Raster to render in D3.Digital Image Processing in Remote Sensing.This package provides : access to a pre-downloaded subset of Natural Earth v4.1.0 (March 2018) vector data commonly used in world mapping. Water Availability, Quality, Accessibility and Monitoring An R package to hold and facilitate interaction with Natural Earth map data.Hydrometric Analysis – Uncertainty Analysis.Hydrometric Analysis – Feasibility and design.Hydrometric Network – Monitoring and Optimization.Hydrometric Analysis – Flow Gauge Ratings.nearth-package: nearth: Natural Earth local data access nearthpath: Retrieve the Natural Earth path readnearth: Read one or more Natural Earth data.
#Naural earth raster in r full#
GIS Application and Mobile GIS Development findnearthrasters: Find the full path for a raster dataset findnearthvectors: Find the full path for a vector dataset hasnearth: Test for the existence of a Natural Earth path in R's.Refine R Markdown Reports with Images and Basemaps 3.1 Intro to Lidar Data 3.2 Lidar Raster Data in R 4.
#Naural earth raster in r code#
Clean Code & Getting Help with R 2.1 Get to Know R 2.2 Time Series Data in R SECTION 3 LIDAR RASTER DATA IN R 3.

The target dataset and then tries to find the rectangular region of The issue here is that the warper process by rectangular regions of The whole explanation from gdal-devA is worth including here:Īdding -wo SAMPLE_STEPS=1000 fixes it (1000 is experimentally found.ġ00 was almost perfect, and then I just tried 1000). I also verified that problem is not caused by the lanczos resampling but "-r average" produces the same artifact.Īs mentioned in an answer by Andre Joost, the issue can be fixed by adding parameter -wo SAMPLE_STEPS=1000 into the gdalwarp command. My main problem right now is that the raster-object is colored as if the integer value were an intensity. I believe that the issue is real and you can file next a ticket into GDAL bug tracker. I can reproduce the error with another Natural Earth image and GDAL version 2.0-dev.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
